|
| SCIENCE | MATTER | SOLAR SYSTEM | PLANETS | ATMOSPHERE | WIND and TEMPERATURE | HUMIDITY | WEATHERING | SOIL | SEASONS | MASS WASTING | SEASONS and CLIMATE | WIND WORK | STREAMS | LAND FORMS | GROUND WATER | CAVES/KARST | THE OCEAN | TIDES & ESTUARIES | WAVES | GLACIERS | GLACIAL LANDFORMS | VOLCANOES | VOLCANOES | CHON | PLATE TECHTONICS | EARTHQUAKES | ROCKS | CLIMATE CHANGE |
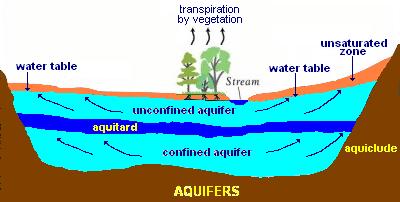
Ground water - water under ground, usuassly below soil level. Upper level is usually polluted and undrinkable.
porosity - volume of space available in a substance. Ground has about 40%.
permeability - ability of a substance to allow water to pass through it.
aquifer (water carrier) porous permeable layer of rock/sediment that yields water.
aquiclude (water stop/shut) layer of earth that will not yield water.
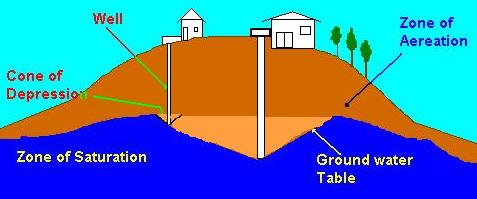
well - hole dug to yield water. Most dug by drill or auger today, in achient times may have been a room sized hole with a descending ramp at the side.
spring - area that has a natural emmissin of water.
unconfined aquifer - water not trapped (easily polluted).

confined aquifer (artesion system) - water trapped between two aquicludes.
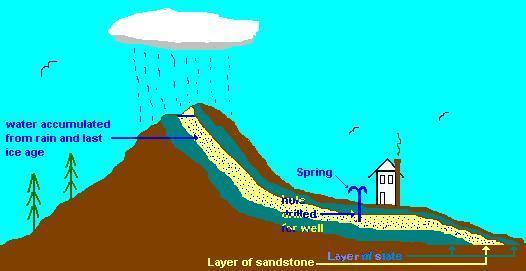
Freebie from the text.