Relative humidity - amout of water in the air divided by the
amount of water the air can hold.
amount of moisture in air________
amount of moisture that air can hold
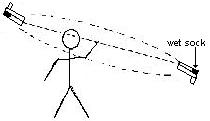
This can be determined by use of a "sling", two thermometers fixed togather,
with a damp "sock" on the end of one. The user swings the "sling" around
several times then measures the difference in temperatures and then looks up the
relative humidity on the chart.
The lower the humidity, the faster the rate of evaporation.
The amount of water air can hold is dependent on temperature
of the air. Warmer air holds more moisture.
At the saturation point the air can hold no more water.
Dew Point - temperature at saturation.
Air cools as it rises until it reaches the Dew Point.
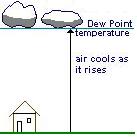
Clouds (drops of water) form when air is cooler than Dew Point.
If many of the drops get togather, they gain weight and fall as rain, sleet,
hail, snow.
Mammals spends energy to keep warm i.e. exercising to keep warm when
its cold.
Sweat cools a mammals body by evaporating. If the humidity is high the body
feels sticky/damp, if it is low it feels dry. The lower the humidity, the more
comfortable a person is.
Climate is the average weather of a local.