- a. Adding mass to the ground. Water is heavy
b. Lubrication. It makes the ground slippery
c. It causes clay minerals to swell making the slope steeper and super slippery.
(sheets of plastic are sometimes placed over a slope and/or drainage pipes are
installed to prevent water from soaking into the ground)
2. Types of Mass Wasting are:
- a. Fall - happens quickly, caused by something i.e. animal, long exposure
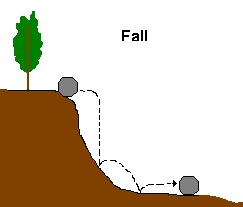
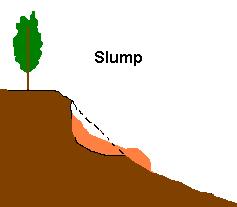
b. Slump - failure on a curved surface - takes a few minutes
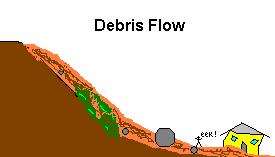
c. Debris Flow - dirt water mixture that tures into new stuff, a slurry, somewhat
like a cake batter that can carry large objects i.e. automobiles, trees, boulders,
down hill at very high speeds.
d. Creep - very slow movement (years) envolving the surface of soil. Water swells
the soil and pushes it out. Small peices move down hill at a slow rate. This bends
things over in the direction of the slide. Plants such a trees want to grow straight up
which results in a bend in the trunk, inanimate objects like a fence post are just
bent toward the downhill slope.

Geological Work - moving material from one place to another.
- 1. Steps - the following steps happen togather, but require different levels of energy
to accomplish
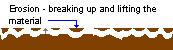
- a. erosion - this is the loosening, lifting, and removing the material, and it
requires the most energy
b. transportation - this is the moving of the material from one point to another,
and requires less energy

c. deposition - this is dropping the material and requires no energy

2. Agents - things that do geological work, stong agent - river moving stuff into lake, glacier
moving boulders
- a. wind - horizontal movement of air
b. streams - moving water in a channel or the channel itself (regardless of size)
c. waves - movement of energy transmitted by water onto land
d. glaciers - large mass of ice that forms on land from recrystalized
snow, needs to be 50 meters thick to move material