|
COURSE LECTURE NOTES:
|
SCIENCE | MATTER |
SOLAR SYSTEM |
PLANETS | ATMOSPHERE |
WIND and TEMPERATURE |
HUMIDITY | WEATHERING |
SOIL |
SEASONS | MASS WASTING |
SEASONS and CLIMATE |
WIND WORK |
STREAMS | LAND FORMS |
GROUND WATER |
CAVES/KARST | THE OCEAN |
TIDES & ESTUARIES |
WAVES | GLACIERS |
GLACIAL LANDFORMS |
VOLCANOES | VOLCANOES |
CHON | PLATE TECHTONICS |
EARTHQUAKES |
ROCKS |
CLIMATE CHANGE |
STREAMS
Stream - any sized channelized flow of water or the channel it flows in.
Things that control stream velocity
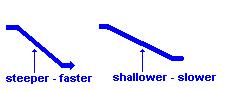
1. stream gradient - slope, the steeper the gradient the faster the stream velocity
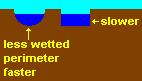
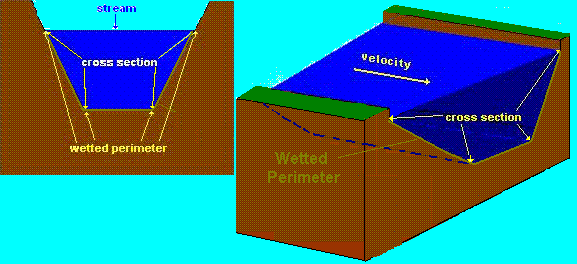
2. wetted perimeter - amount of channel the stream touches, the less the faster faster the stream velocity

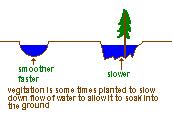
3. smoothness - less friction, the smoother the channel the faster the stream velocity
4. discharge - the amount of water flowing, the more discharge the faster the stream velocity. Discharge equals the choss section of the stream at a point times the stream velocity (in the U.S, A. usually expressed in cubic feet)
Stream work
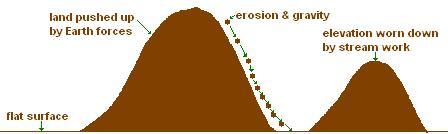
Stream work is trying to make the Earth flat. As plate techtonics causes the land to rise, streams tend to cut it down.
Steps in stream work (close to identical to work done by wind)
1. erosion- breaking and lifting - takes the most work
a. direct lifting

b. abrasion
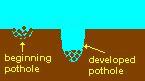
pot holing
2. transportation
a. bed load - big stuff, sand to bolders,rolling, sliding, saltation.
b. suspended load - small stuff, never gets back to bed
c. dissolved load - salts, ions, pollution
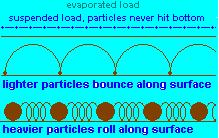
3. deposition- heavest stuff falls out first as stream slows
a. bed load
b. suspended load
c. dissolved load, water must evaporate in order to precipitate this load.
LAND FORMS CREATED BY STREAM ACTION
1. Erosional
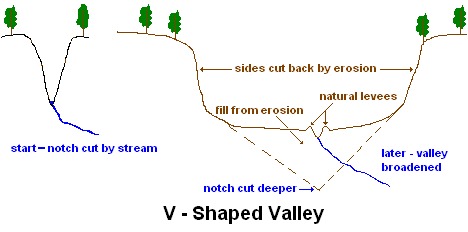
a. V - shaped valley - a valley cut by a stream. It begins as a narrow cut and then is widened out by erosion/mass wasting as the stream cuts deeper
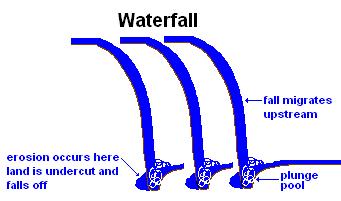
b. water Fall - result of stream flowing through a hard layer of rock deposited over a softer layer. Erosin occurs in the plunge pool, face of fall is under cut and falls off. The falls migrate up stream. Some communities, such as Niagra, have attempted to halt this migration by using concrete.
2. Depositional
a. delta - deposition of soil as a stream encounters the edge of a lake or ocean and slows.
 |  |
b. alluvial fan - the soil/debris washed down from a mountain by a stream, Forms a V - shaped fan.
b.(1)bajada - a series of connected alluvial fans, such as those north of Chaffey.

c. playa - dry lake bed

3. Both Erosional and Depositional
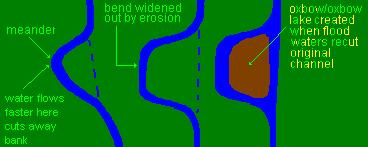
a. meander - bend in a stream. It sometumes widens and becomes an oxbow lake.
Home
 Page Visits
Page Visits