|
COURSE LECTURE NOTES:
|
SCIENCE | MATTER |
SOLAR SYSTEM |
PLANETS | ATMOSPHERE |
WIND and TEMPERATURE |
HUMIDITY | WEATHERING |
SOIL |
SEASONS | MASS WASTING |
SEASONS and CLIMATE |
WIND WORK |
STREAMS | LAND FORMS |
GROUND WATER |
CAVES/KARST | THE OCEAN |
TIDES & ESTUARIES |
WAVES | GLACIERS |
GLACIAL LANDFORMS |
VOLCANOES | VOLCANOES |
CHON | PLATE TECHTONICS |
EARTHQUAKES |
ROCKS |
CLIMATE CHANGE |
CAVES/ KARST TOPOGRAPHY
Karst topography is a three-dimensional landscape shaped by the dissolution of a soluble layer or layers of bedrock, usually carbonate rock such as limestone or dolomite.
Cave - natural opening underground > 0.5 cm created from dissolving rock. If smaller than 0.5 cm water clings to the sides instead of flowing. A cave is a small ecosystem. Usually formed limestone or marble. The chemical process is adding acid to rock to form calcium, water and carbondioxide: The process works both ways.
CaCo3 + 2H+ <---->Ca+ + H2O +CO2
rock ...... acid .......... ion .. water ... gas
disolve<----->deposit
make caves <-----> form speleothems
1. Formation and demise
Steps in the formation and demise of a desolution cave:
a. initial fractures form. fairly easy in limestone, harder in Marble, may require seismic activty, creats two surfaces for dissolving rock.

b. rock dissolves rock along surfaces of cracks

c. Some holes (tunnels) continue to grow and form sponge works while others are abandoned It depends on water flow. This is a complex step, it and steps 4 & 5 can happen simultaenouusly in the same cave.
d. cave can flll or empty of water or mud. calsite is deposited as speleothems.
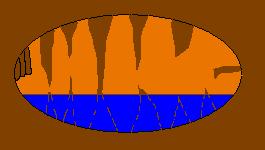
e. death - the cave becomes open to the surface and begins to die from the results of changing temperatures, atmospheric conditions, and animal/human polution.

2. speleothems - cave forms
a. drip stone
1) straw - all drip stones start as a straw. A drop of water seeps throught to the cave ceiling and either drops or evaporates leaving a small ring deposit of calcium. the straw may stay as a straw or grow into a stalactite or stalagmite
2) stalactite - descends from cave ceiling

3) stalagmite - grows up from cave floor. This form cannot exist unless a straw forms first.

4) column - a stalactite and stalagmite that have joined

b. flow stone
1) canopy - projection that formed over another substance that was later removed.

2) draperies- folds hanging from sides of cave
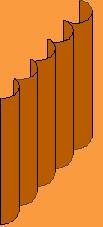
c. irregular
1) popcorn

2) helectites
3) grapes

Home
 Page Visits
Page Visits