|
COURSE LECTURE NOTES:
|
SCIENCE | MATTER |
SOLAR SYSTEM |
PLANETS | ATMOSPHERE |
WIND and TEMPERATURE |
HUMIDITY | WEATHERING |
SOIL |
SEASONS | MASS WASTING |
SEASONS and CLIMATE |
WIND WORK |
STREAMS | LAND FORMS |
GROUND WATER |
CAVES/KARST | THE OCEAN |
TIDES & ESTUARIES |
WAVES | GLACIERS |
GLACIAL LANDFORMS |
VOLCANOES | VOLCANOES |
CHON | PLATE TECHTONICS |
EARTHQUAKES |
ROCKS |
CLIMATE CHANGE |
THE SOLAR SYSTEM
The Solar System consists of 6 layers: the Sun, planets & their moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, Dwarf Planets/Keiber Belt Objects. (Acoustical waves were used to identify these)
1. The Sun – It is a yellow medium star (A star is spherical gas ball held together by gravity.)
It contains 99% of matter/mass of the system. It produces all visible light; all other light (i.e. from the Moon) is reflected.
It is made up of Hydrogen and Helium. Peak energy of the Sun in the yellow color frequency. It produces light/energy by fusion that is by the creation of larger atoms from smaller atoms. i.e.
4H atoms -- 1He atom.
H has a mass of 1 (amu), He has a mass of 4 (amu)
2 protons are converted to neutrons
H -- He + heat
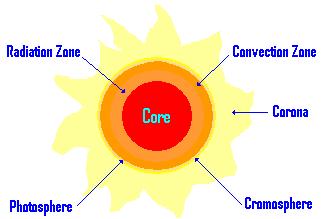
Layers of the Sun:
Core = place where fusion occurs, where energy is created
Radiation Zone = movement of energy, waves of energy move out
Convection Zone = movement of energy hot material rising and cool material sinking.

Photosphere = where most of light is created (by heat agitating atoms).
Chromosphere = red layer
Corona = irregular shaped crowning layer of Sun’s atmosphere.

2. Planets and their moons – planets are spherical objects that orbit the Sun. Moons are spherical (the larger ones) objects that orbit planets. When large enough they become spherical due to their mass.(Galileo discovered the 4 moons, other than ours, in the Solar System orbiting Jupiter).
3. Asteroid – rock orbiting the Sun. Most are in the Asteroid Belt outside of Mars, but some can be “Near Earth” objects
4. Meteoroid – rock in space. (Meteor is a meteoroid entering our atmosphere and making a streak of light. Meteorite is a meteoroid that hits the Earth)
5. Comet – ice (made up of different gasses i.e. H2O, CO4, CH4, and others) and rocks. Usdually thr rocks are dust particles to small boulders; these may be the source of meteroids.
6. Dwarf planets and other Keiper Belt Objects – icy debris, orbits vary; these may be the source of some comets.
Back to Homepage
 Sight Visits
Sight Visits