|
COURSE LECTURE NOTES:
|
SCIENCE | MATTER |
SOLAR SYSTEM |
PLANETS | ATMOSPHERE |
WIND and TEMPERATURE |
HUMIDITY | WEATHERING |
SOIL |
SEASONS | MASS WASTING |
SEASONS and CLIMATE |
WIND WORK |
STREAMS | LAND FORMS |
GROUND WATER |
CAVES/KARST | THE OCEAN |
TIDES & ESTUARIES |
WAVES | GLACIERS |
GLACIAL LANDFORMS |
VOLCANOES | VOLCANOES |
CHON | PLATE TECHTONICS |
EARTHQUAKES |
ROCKS |
CLIMATE CHANGE |
SOIL
Soil is an essential ingredient to life on the continents. Without it there would be no
life there.

1. The following are notes from the movie "Planet Under Pressure",
"The Living Soil"
Soil is an amazing substance, a self-sustaing machine that, in nature,
requires no matainence. Nature uses
the turn-over system by
recycling most nutrients. The forest have existed for millennia without artificial help.
To begin with, rock contains most of the
nutrients necessary for plant growth, but it is not readily available
in the rock form.
Weathering breaks the rock down into smaller peices, until it gets to the smallest/finest;
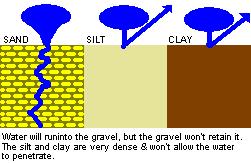
sand, silt and clay.Clay is the finest. But, sand, silt, and clay alone do not make soil.
Sand will not retain
water and silt and clay are too dense (pores are too small) to allow much
water in.
Another Ingredient is required. That is "humus". Humus is the result of decaying
plant life. The plants and/or
leaves die. Then they disintegrate, decompose and finally turn
into humas. Without humus there would be no
forests, no plant life at all. It is a case of the living,
thriving on the dead. (sound familiar? like maybe the "circle
of life?") Humus is a store house of nutriants.

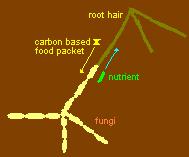
Plants really do not do a good job of taking in nutriants. The root hairs are not big enough, so millions of years
ago plants formed a symbiotic relationship with fungi. This extended their reach a thousand fold. In return the
plant provides carbon based food to the fungi.
A problem still exists. Nitrogen and potassium are required for plant growth. There is plenty of nitrogen
available in the atmosphere, but not in readily useable form. Nitrogen is a stubborn element. Its molecule
is made up of two tightly bound attoms. The roots and fungi do not have the energy to break the bond to
release the atoms. this requires a 'soil mechanic'. This is a bacteria called a nitrogen fixer. The bacteria
absorbs nitrogen from the atmosphere and cracks it for its own use. The fungi then eat the bacteria and/or
its waste
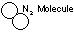
In order to obtain nitrogen faster plants obtain it from humus. This takes specialized organisms called
decomposers, "the undertakers of the world". These organisms break down the nitrogen in the humus
so that there is an ample supply for
the plants. This is the circle, from live plants to humus and back to
living plants.
The system slows the release of nitrogen by forming modules of small particles of humus
surounded by particles of silt and clay. The humus releases particle of sugar that glue the silt and clay to it.
The more glue the more particles. The modules join togather to form larger modules until they make up
the top soil of the area. Insects also eat the humus and pass the waste product to the fungi.
Soil is a system in a delicate balance. Humans have upset that balance in several ways; by over intensifying
planting, by destroying the humus by plowing to deep, by not rotating crops, and by use of chemicals. we
can assemble the ingrediants of soil and grow crops in it, but nothing on the scale of nature. And, it is a one
way trip. At the end the nutriants are lost to the system and must be replaced.
2. Soil Layers
O - Horizon
organic liter
humus forms here
A- Horizon has humas
leaching and eluviation occur from rainfall
E - Horizon same as A- horizon except no humus
B - Horizonlayer of deposition of ions
small particles, red or green
C - Horizonweathering parent material
K - HorizonContains CaCO3 = caliche - white
3. Koppen's Climate Classifications
Climate is the general local weather pattern, and is a result of the circulation of the atmosphere. Soil development
depends on climate. the faster the erosion of rock, the faster the soil builds.
Climate A - rain forest
Climate B - desert, hot, dry
Climate C - has winter and summer, winter is mild
Climate D - has winter and summer, winter is severe
Climate E - Polar desert, very cold occasional storms
Climate H - Mountain climates that vary with altitude
4. Soil types
A - soil type = Ultisol - most weathering, not good for farming
B - soil type = Aridisol - desert, not much littering
C & D - soil type = Alfisol - great for growing stuff
E - soil type = Inceptisol
Home
 Page Visits
Page Visits